Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for maintaining overall health, benefiting heart function, brain health, and reducing inflammation. However, as with most nutrients, balance is key. While rare, consuming excessive amounts of omega-3 can lead to adverse effects. Here's how to recognize the signs and maintain the right balance.
1. Increased Bleeding and Bruising
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, are known for their blood-thinning properties, which help reduce the risk of blood clots. However, excessive intake can amplify this effect, leading to prolonged bleeding from minor cuts or frequent bruising.
📚 Reference: An observational study done by Lund University in Sweden concluded that high doses of omega-3 supplements increased bleeding time, though the effects were typically mild and reversible (source).
 2. Gastrointestinal Distress
2. Gastrointestinal Distress
Overconsumption of omega-3s, especially from supplements, can cause digestive issues such as diarrhea, nausea, or bloating. These symptoms are often linked to the oil-based nature of the supplements.
📚 Reference: Research done by Dr. Bradberry at Creighton University highlighted adverse events occurring in about 1% of patients. This included diarrhea and flatulence (source).
3. Lowered Immune Response
While omega-3s are anti-inflammatory, excessive consumption can suppress your immune response, potentially making you more susceptible to infections. Maintaining a balanced omega-6 to omega-3 ratio is crucial to avoid this effect.
📚 Reference: A 2019 review 'Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Immune Cells' details how high doses of omega-3 can inhibit immune cell functions, particularly in individuals with already low immunity (source).
4. Potential Blood Sugar Increases
Some studies suggest that very high doses of omega-3 may slightly raise fasting blood sugar levels, though the evidence is mixed and usually applies to doses far beyond the typical recommendation.
📚 Reference: A 2021 meta-analysis noted that omega-3 supplementation had a negligible but detectable impact on fasting glucose in individuals with type 2 diabetes (source).
5. Vitamin E Depletion
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly from fish oil, can deplete vitamin E levels in your body over time, as vitamin E is needed to prevent omega-3 oxidation. Without adequate vitamin E, your body may experience oxidative stress.
📚 Reference: A large 2020 meta-analysis demonstrated the interplay between omega-3 and vitamin E, emphasizing the need to balance both to avoid oxidative damage (source).
How Much Omega-3 Is Too Much?
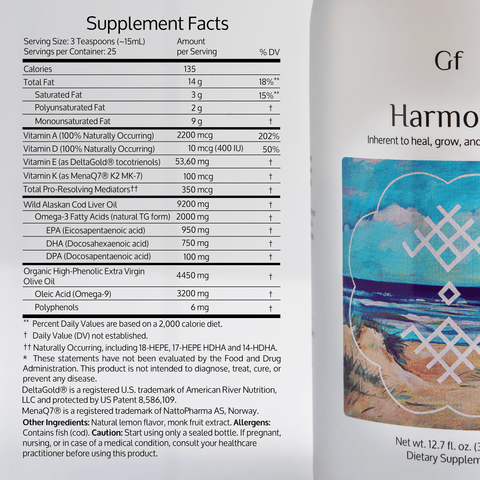
The FDA considers up to 3 grams (3,000 mg) of combined EPA and DHA per day from supplements to be safe. However, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) suggests a limit of 5,000 mg per day. Stick to the dosage recommended by your healthcare provider to avoid adverse effects.
Finding the Right Balance
Omega-3 fatty acids are vital for your health, but overdoing it can lead to side effects. Be mindful of your intake from both diet and supplements. If you're unsure about the right dosage, consult a healthcare professional to personalize your omega-3 needs.