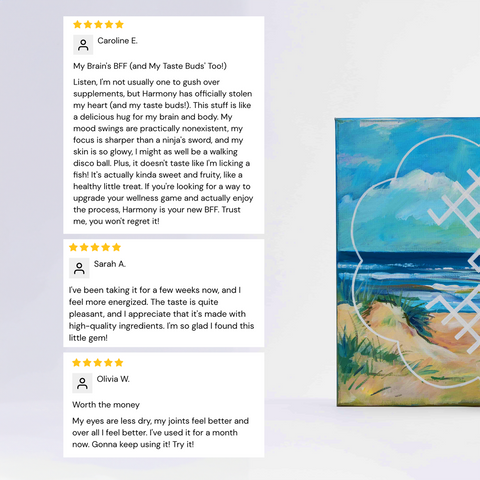
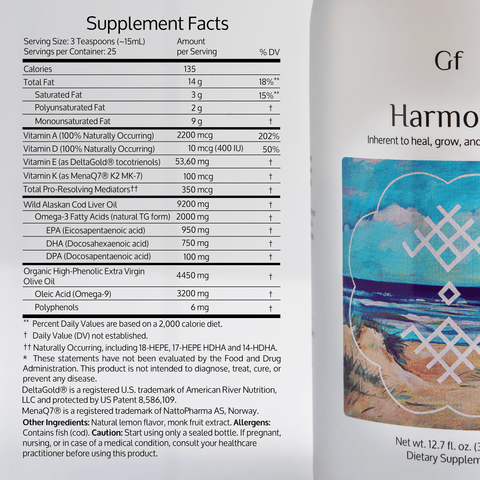
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for maintaining good health. They support heart health, brain function, reduce inflammation, and even improve skin. Despite their importance, many people unknowingly suffer from Omega-3 deficiency. In this post, we’ll explore five common warning signs that could indicate you’re not getting enough Omega-3s.

1. Dry Skin and Hair
One of the earliest signs of Omega-3 deficiency is noticeably dry, flaky skin and brittle hair. Omega-3s play a crucial role in maintaining the skin’s hydration and elasticity by supporting the skin’s natural oil barrier. When levels are low, the skin loses moisture, leading to dryness, while hair may become brittle and prone to breakage.
2. Joint Pain and Stiffness
Joint pain and stiffness, particularly in people with inflammatory conditions like arthritis, may be related to low levels of Omega-3. Omega-3s help to reduce inflammation, which can cause swelling and discomfort in the joints. Without enough Omega-3, inflammation can worsen, leading to increased pain and reduced joint mobility.
Studies have shown that Omega-3 supplementation can help reduce symptoms of arthritis and other inflammatory conditions (source).
3. Brain Fog and Memory Issues
Omega-3s, particularly DHA, are vital for brain function and cognitive performance. A deficiency can contribute to problems like memory lapses, difficulty focusing, and "brain fog." DHA supports the development and maintenance of the brain’s neurons, improving communication between cells. Without sufficient Omega-3 intake, cognitive function can decline.
Research indicates that regular consumption of Omega-3s improves brain health and mental clarity (source).

4. Mood Swings and Depression
Omega-3 deficiency has been linked to mood disorders like depression, anxiety, and irritability. Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, help regulate neurotransmitters in the brain, including serotonin, which is vital for mood stabilization. Low levels of Omega-3 can lead to mood swings or even symptoms of clinical depression.
Several studies support the role of Omega-3 supplementation in reducing the symptoms of depression and improving overall emotional well-being (source).
5. Vision Problems
Omega-3s play a key role in maintaining eye health, specifically through DHA, which is found in high concentrations in the retina. A lack of Omega-3s can lead to dry eyes, blurry vision, or a higher risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Ensuring an adequate intake of Omega-3s can help protect against these vision issues.
Research has shown that Omega-3 fatty acids may help prevent AMD and improve overall eye health (source).
How to Restore Omega-3 Levels in Your Body
If you’ve identified one or more of these symptoms in yourself, there are several effective ways to increase your Omega-3 intake. Here are some tips:
- Increase Your Consumption of Fatty Fish: Fish such as salmon, sardines, and mackerel are rich sources of EPA and DHA, the most effective forms of Omega-3. Aim for two servings per week.
- Incorporate Plant-Based Omega-3 Sources: Flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts contain ALA, a plant-based form of Omega-3 that can support overall health.
- Consider Omega-3 Supplements: Fish oil, krill oil, or algae-based Omega-3 supplements can fill the gap if you’re not consuming enough through your diet.
Conclusion
Omega-3 deficiency can manifest in a variety of ways, from dry skin and brittle hair to joint pain, mood disorders, and even vision problems. Fortunately, addressing this deficiency is simple—by eating more Omega-3-rich foods or taking a supplement, you can restore your levels and enjoy the numerous health benefits of these essential fatty acids. If you suspect you’re Omega-3 deficient, start incorporating more of these foods into your diet today.