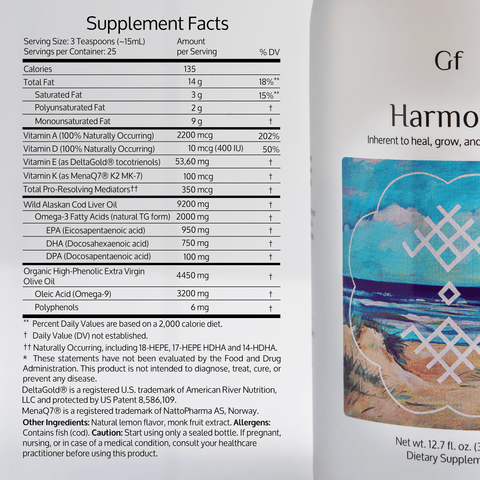
Heart health is a top concern for many, and managing cholesterol is key to reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease. Omega-3 fatty acids, renowned for their anti-inflammatory and heart-protective properties, are often touted as beneficial for cholesterol management. But can they truly help lower cholesterol levels? Let’s dive into the science.
1. Understanding Cholesterol and Its Types
Cholesterol, a lipid found in the blood, is essential for various bodily functions, including hormone production and cell membrane formation. However, an imbalance in cholesterol levels can lead to health problems:
- LDL Cholesterol (Low-Density Lipoprotein): Known as “bad cholesterol,” high levels can result in plaque buildup in arteries.
- HDL Cholesterol (High-Density Lipoprotein): Referred to as “good cholesterol,” it helps transport excess LDL to the liver for elimination.
- Triglycerides: A type of fat in the blood, elevated triglyceride levels are associated with an increased risk of heart disease.
 2. How Omega-3 Impacts Cholesterol and Heart Health
2. How Omega-3 Impacts Cholesterol and Heart Health
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), are found in fatty fish and fish oil supplements. ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), a plant-based omega-3, is found in flaxseeds and walnuts. Here’s how they influence cholesterol levels:
A. Lowering Triglycerides
Omega-3 fatty acids are highly effective at reducing triglyceride levels:
- Mechanism: Omega-3s reduce the production of very-low-density lipoproteins (VLDL), which carry triglycerides in the bloodstream (source).
- Evidence: Studies have shown that fish oil supplementation can lower triglycerides by 15–30%, depending on dosage and individual health factors (source).
B. Impact on LDL Cholesterol
While omega-3s excel at lowering triglycerides, their effect on LDL cholesterol is more nuanced:
- Some studies suggest a slight increase in LDL levels with high-dose fish oil supplementation, though the LDL particles may become larger and less harmful (source).
- This increase in particle size is linked to a lower risk of cardiovascular events.
C. Improving HDL Cholesterol
Omega-3s may help boost HDL cholesterol levels:
- A review of clinical trials found that omega-3 supplementation modestly increased HDL levels, enhancing the body’s ability to remove LDL from the bloodstream (source).
3. Omega-3 and Plaque Formation
Omega-3 fatty acids don’t just address cholesterol levels; they also prevent harmful processes associated with atherosclerosis:
- Reducing LDL Oxidation: Oxidized LDL is more likely to stick to artery walls. Omega-3s’ antioxidant properties can help prevent this process (source).
- Decreasing Inflammation: Chronic inflammation contributes to plaque buildup. Omega-3s reduce the production of inflammatory molecules, protecting arterial health (source).
4. Omega-3 vs. Statins for Cholesterol Management
Statins are widely prescribed to lower cholesterol, but how does omega-3 compare?
- Statins are highly effective at lowering LDL cholesterol but have minimal impact on triglycerides.
- Omega-3s primarily target triglycerides and inflammation, making them a complementary therapy for overall heart health.
 5. Choosing the Best Omega-3 Sources
5. Choosing the Best Omega-3 Sources
For optimal cholesterol management, quality matters:
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources of EPA and DHA.
- Fish Oil Supplements: Choose molecularly distilled products to ensure purity and potency. Goodfatts Cod Liver Oil is an excellent option.
- Plant-Based Options: Flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts provide ALA, though conversion to EPA and DHA is limited.
6. How Much Omega-3 Do You Need?
The American Heart Association recommends:
- For General Heart Health: Two servings of fatty fish per week.
- For Lowering Triglycerides: 2-4 grams of EPA and DHA daily, under a doctor’s supervision (source).
7. Incorporating Omega-3 Into Your Diet
Simple ways to boost your omega-3 intake:
- Add grilled salmon to your meals.
- Drizzle flaxseed oil over salads.
- Take a daily cod liver oil supplement for convenience.
Omega-3 fatty acids are a valuable ally in maintaining healthy cholesterol levels and supporting overall cardiovascular health. By incorporating them into your diet, you can take proactive steps toward a healthier heart.