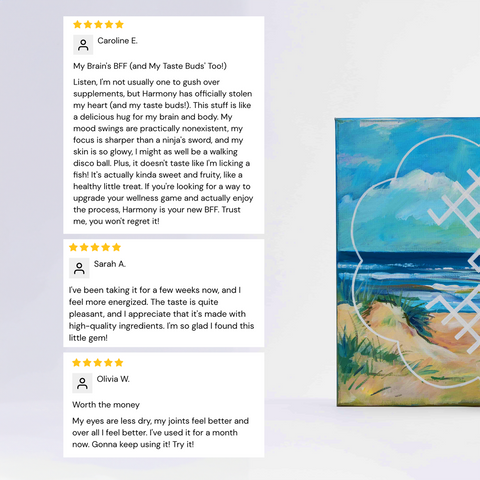
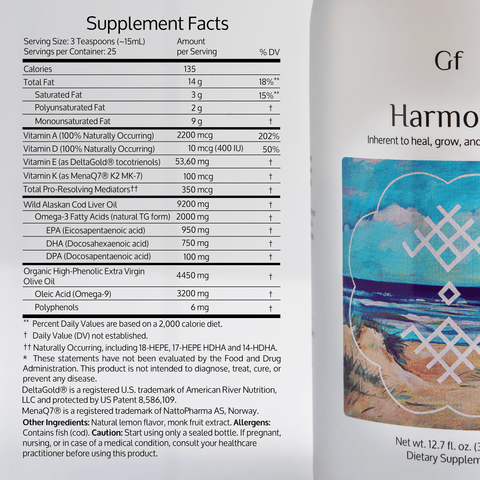
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for heart, brain, and inflammatory health. Not all Omega-3s are created equal, though—animal-based sources like cod liver oil contain EPA and DHA, while plant-based sources primarily provide ALA. Here, we’ll explore the differences between these types and look at the science behind their health benefits.
1. Types of Omega-3: EPA, DHA, and ALA
 The three main types of Omega-3 fatty acids are EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid), DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), and ALA (alpha-linolenic acid). Animal-based Omega-3s (found in cod liver oil) provide EPA and DHA, while plant-based sources are high in ALA.
The three main types of Omega-3 fatty acids are EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid), DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), and ALA (alpha-linolenic acid). Animal-based Omega-3s (found in cod liver oil) provide EPA and DHA, while plant-based sources are high in ALA.
- Cod Liver Oil (EPA and DHA): EPA and DHA are the active forms of Omega-3 that are readily absorbed by the body. Studies show that EPA and DHA support heart, brain, and vision health, with EPA playing a role in reducing inflammation and DHA supporting cognitive function (NIH, 2023).
- Plant-Based Omega-3 (ALA): ALA is mainly sourced from flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. While beneficial, it must first convert to EPA and DHA to provide the same heart and brain health benefits. Unfortunately, this conversion rate is low, with only about 5-10% of ALA converting to EPA and DHA, according to research (Eur J Ntr, 2021).
2. Bioavailability: How Well Are Omega-3s Absorbed?
Bioavailability, or the body’s ability to absorb nutrients, varies significantly between cod liver oil and plant-based Omega-3s.
-
Cod Liver Oil (EPA and DHA): EPA and DHA in cod liver oil are directly bioavailable. This is beneficial for those needing immediate Omega-3 support, as it’s efficiently used without conversion.
-
Plant-Based Omega-3 (ALA): Since the body needs to convert ALA to EPA and DHA, much of its Omega-3 potential is lost. Studies indicate that, on average, only about 5% of ALA is converted to EPA, with even less becoming DHA (NIH, 2009).
3. Health Benefits: Animal vs. Plant-Based Omega-3
While both sources offer health benefits, cod liver oil’s high EPA and DHA content gives it an edge in specific areas.
-
Cod Liver Oil for Heart Health: Cod liver oil’s high levels of EPA and DHA are linked with lower blood pressure, triglyceride levels, and overall cardiovascular improvement. Studies reveal that regular intake of EPA and DHA can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease by as much as 25% (Int J Mol Sci, 2020).
-
Cod Liver Oil for Brain Health: DHA is particularly important for brain health, supporting cognitive functions and mood regulation. Research has shown that DHA supplementation is linked to improved cognitive health and a reduced risk of neurodegenerative diseases (Front Nutr, 2022).
-
Plant-Based Omega-3 for General Wellness: ALA has antioxidant properties that benefit skin, hair, and general wellness, although it lacks the potency of EPA and DHA for specific health outcomes (Molecular nutrition & food research, 2019).
4. Sustainability and Sourcing Considerations

Sustainability often plays a role in choosing Omega-3 sources. Cod liver oil and plant-based Omega-3s both have unique environmental impacts.
-
Cod Liver Oil: Cod liver oil sourced from sustainable fisheries is an eco-conscious choice for Omega-3s. Opt for brands like ours certified by the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) to ensure sustainable harvesting practices (MSC, 2023).
-
Plant-Based Omega-3: Plant sources like flaxseed and chia have a lower environmental impact. They are also preferred by vegetarians and vegans looking for Omega-3 alternatives without fish or animal byproducts.
5. Who Might Benefit More from Each Type?
-
Cod Liver Oil: Cod liver oil is ideal for individuals needing high levels of EPA and DHA, such as those with heart concerns or cognitive health needs. Research shows that the bioavailable EPA and DHA in cod liver oil may be especially beneficial for managing triglycerides, inflammation, and neuroprotection (NIH, 2023).
-
Plant-Based Omega-3: ALA is suitable for those focusing on general wellness or seeking vegetarian-friendly Omega-3 options. Although it doesn’t convert efficiently to EPA and DHA, ALA is a valuable addition to a healthy diet for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties (Br J Nutr, 2011).
Conclusion
Cod liver oil, with its high EPA and DHA content, provides potent Omega-3 benefits for cardiovascular, cognitive, and inflammatory health. In contrast, plant-based Omega-3 offers ALA, an important but less efficient Omega-3 for similar benefits.