Olive oil, particularly extra virgin olive oil (EVOO), has been celebrated for its health benefits for centuries. But what exactly makes it a "superfood"? The answer lies in its unique chemical composition, which provides a variety of health-boosting properties. Let’s dive into the chemistry of olive oil and explore why it deserves a place in your daily diet.
1. Oleic Acid: The Heart-Healthy Monounsaturated Fat
One of olive oil’s primary components is oleic acid, a monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA) that constitutes about 55-83% of its total fat content. Oleic acid has been shown to:
- Reduce LDL ("bad") cholesterol while increasing HDL ("good") cholesterol.
- Lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
A 2011 study from Biomolecules confirms that diets rich in oleic acid can significantly improve heart health (source).
 2. Polyphenols: Nature’s Antioxidants
2. Polyphenols: Nature’s Antioxidants
EVOO contains a variety of polyphenols, such as hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein, which are powerful antioxidants. These compounds help:
- Neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and cellular damage.
- Protect against chronic diseases like cancer and neurodegeneration.
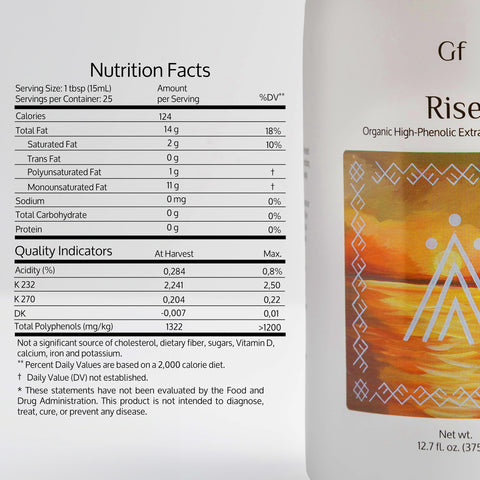
Research in Antioxidants highlights that olive oil polyphenols reduce inflammation and promote overall health (source).
3. Vitamin E: Skin and Cellular Protection
Vitamin E, a fat-soluble antioxidant present in olive oil, contributes to its superfood status by:
- Protecting skin cells from oxidative damage caused by UV exposure.
- Supporting immune function and reducing the risk of certain chronic diseases.
According to a study published in Dermato-endocrinology, vitamin E supplementation improves skin health and cellular longevity (source).
4. Squalene: A Unique Compound for Skin and Cancer Prevention
Squalene, a lesser-known compound found in olive oil, has unique properties that set it apart:
- Acts as a natural moisturizer for the skin.
- Shows potential in preventing certain types of cancer due to its antioxidant activity.
A recent 2020 study in suggests that squalene’s anticancer properties may be particularly effective in the Mediterranean diet (source).
 5. Phytosterols: Cholesterol-Lowering Plant Compounds
5. Phytosterols: Cholesterol-Lowering Plant Compounds
Olive oil also contains phytosterols, which are plant-derived compounds structurally similar to cholesterol. These compounds:
- Help reduce the absorption of dietary cholesterol in the intestines.
- Improve overall lipid profiles, supporting heart health.
A review in Brazilian Archives of Cardiology indicates that a diet rich in phytosterols significantly lowers LDL cholesterol levels (source).
6. Anti-Inflammatory Properties: The Role of Oleocanthal
Oleocanthal, a phenolic compound found exclusively in EVOO, exhibits powerful anti-inflammatory effects. Its mechanism of action is similar to ibuprofen, blocking inflammatory pathways.
- Reduces chronic inflammation associated with arthritis, cardiovascular diseases, and Alzheimer’s.
Research published in Antioxidants identified oleocanthal as a natural inhibitor of inflammation (source).
7. Why Olive Oil Is a True Superfood
Combining healthy fats, powerful antioxidants, and unique bioactive compounds, olive oil offers a range of health benefits that justify its "superfood" label. Unlike many processed oils, high-quality EVOO retains its natural chemical composition, ensuring maximum health benefits.
How to Maximize the Benefits of Olive Oil
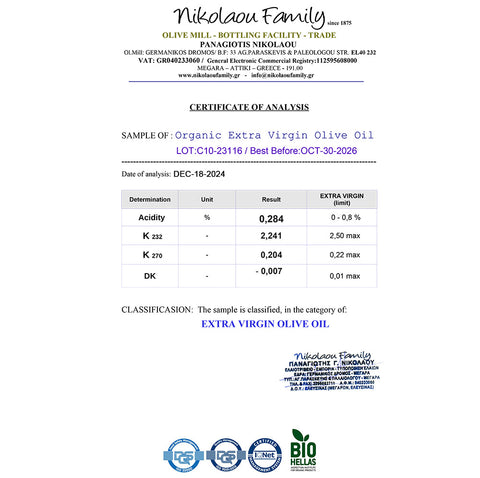
- Choose High-Quality EVOO: Look for polyphenol-rich olive oil like Rise Polyphenol-Rich Olive Oil.
- Store Properly: Keep olive oil in a cool, dark place to preserve its beneficial compounds.
- Use Regularly: Incorporate olive oil into your diet daily for optimal health benefits.